
 Skladovanie plynu
Skladovanie plynu
Gas Storage
In the conditions found in Slovakia, natural rock structures are used to store natural gas underground. Commercial use of these storage facilities in Slovakia started in 1973, when the first cubic meters of natural gas were injected into depleted gas fields. A fundamental advantage in constructing underground storage facilities is the geological and technological knowledge gained from previous production of hydrocarbons from these reservoirs.
- Why are underground storage facilities used to store natural gas?
In periods when less natural gas is used, for instance during the summer months, gas delivered from abroad is stored in underground storage facilities. But when there is not enough gas in the network and demand is high, like in winter, gas can then be withdrawn from them. Although the storage facilities were originally built primarily for seasonal storage, today they are also used to balance hourly, daily, weekly and even monthly inbalances, with its use determined by gas price movements on European exchanges.
The role NAFTA plays in the gas chain is to ensure and provide our customers with storage capacity, especially gas suppliers delivering to end users such as households, industry, gas-fired power plants and transit. Although our activities lack visibility, they nevertheless play an essential role in the life of many households and businesses in Slovakia.
NAFTA’s underground storage facilities are a critical part of the gas infrastructure and key to smooth gas deliveries in Slovakia and Europe, as well as a strategic tool for increasing energy security.
- Storage facility flexibility helps in responding to current market requirements
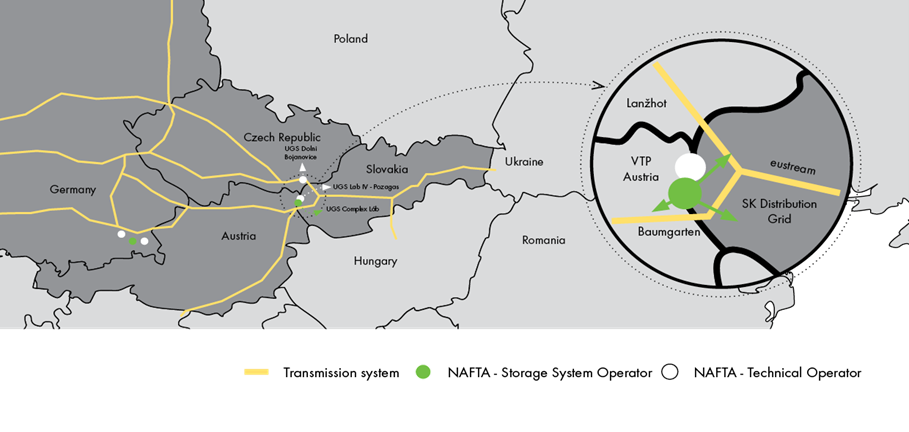
Operating Slovakia’s largest underground storage facility complex, NAFTA has stored natural gas, and been developing the knowledge gained from it, for more than 45 years. We are constantly strenghtening our position in the European market for storage services and been actively working for a long time toward providing safe, reliable and effective use of storage facilities and interconnected networks.We are investing into flexibility of our storage facilities, so that we can switch back and forth between injection and production as needed. NAFTA’s main advantage is in operation of a of storage facility complex connected to other gas distribution and transmission networks and also a virtual trading point in Austria, instead of a single storage facility operation. Located near the borders of three countries, the complex is additionally capable of providing services to all of Central Europe.
NAFTA’s underground storage facilities
NAFTA is an international company with extensive experience in natural gas storage and underground facility development in Slovakia. NAFTA’s professional experience in underground natural gas storage has been effectively applied in international environments and we are using the emerging synergies both technically and commercially. In Germany, we operate underground storage facilities at Inzenham-West, Wolfersberg and Breitbrunn/Eggstätt through NAFTA Speicher, a subsidiary, while in the United Kingdom we are providing our technical-advisory services to the Humbly Grove underground gas storage facility. NAFTA’s efforts to export its know-how are not over and we are also looking at other options for expanding its storage services abroad.
| Company | Country | Underground Gas Storage | NAFTA Technical Operator | NAFTA Storage System Operator | NAFTA Technical -Advisory Services | Working Capacity (TWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAFTA | SK | Complex Lab |
|
| 27.7 | |
| Pozagas | SK | Pozagas |
| 6.9 | ||
| SPP Storage | CZ | Dolní Bojanovice |
| 6.9 | ||
| NAFTA Speicher | DE | Breitbrunn/Eggstätt |
| 11.1 | ||
| Inzenham-West |
|
| 4.8 | |||
| Wolfersberg |
| 4.1 | ||||
| Humbly Grove Energy Limited | UK | Humbly Grove |
| 2.6 |
Today, NAFTA operates and develops technology and services for facilities with more than 64 TWh storage capacity in several European countries, contributing significantly toward secure natural gas supplies.
NAFTA underground storage facilities in Slovakia, Czech Republic and Germany:
 Mapa skladovanie plynu
Mapa skladovanie plynu